Calcium Metabolism: Key Insights & Resources
When working with Calcium Metabolism, the physiological system that keeps calcium levels stable in blood, bone, and cells. Also known as calcium homeostasis, it balances dietary absorption, bone storage, and renal excretion.
Why Calcium Metabolism Matters
Vitamin D, a fat‑soluble vitamin that boosts intestinal calcium absorption works hand‑in‑hand with calcium metabolism. It stimulates the gut to pull more calcium from food, which directly feeds the bloodstream. This influence creates the semantic link: Vitamin D influences calcium metabolism. When levels are low, absorption drops, and the body leans on hormonal pathways to compensate.
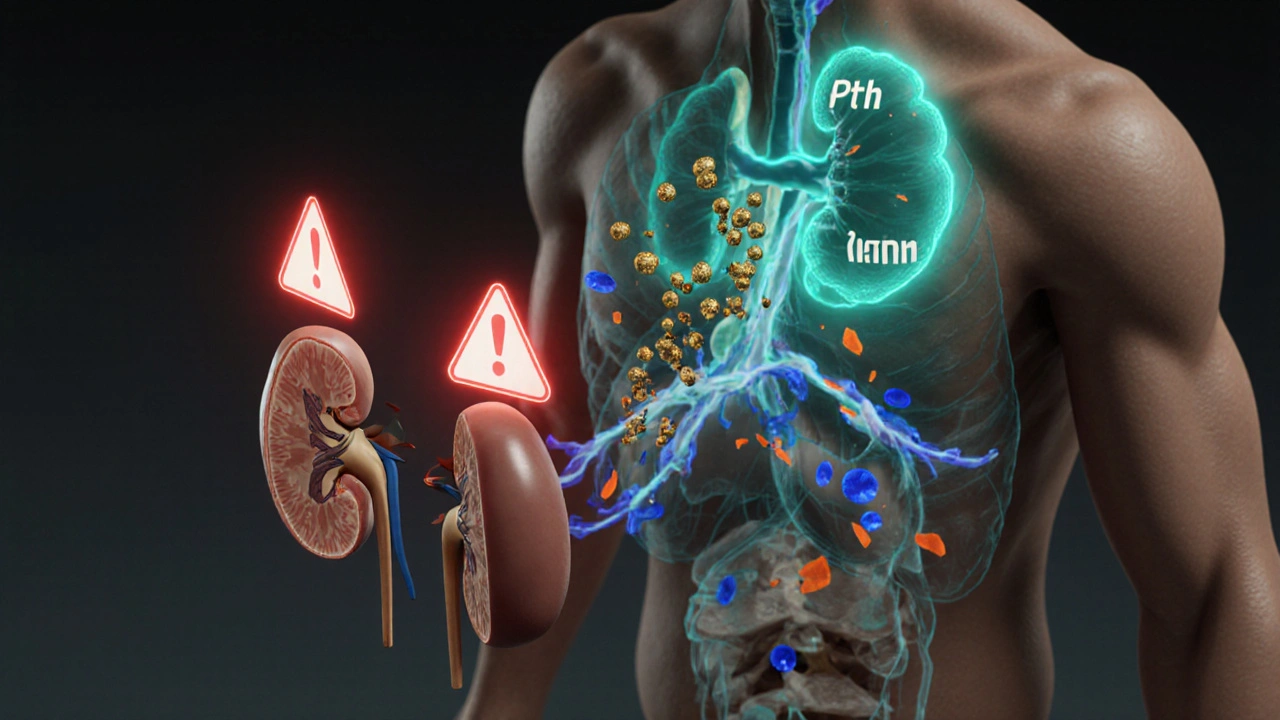
Parathyroid Hormone, a peptide hormone released by the parathyroid glands is the chief regulator of calcium metabolism. It raises blood calcium by prompting bone resorption, increasing kidney reabsorption, and activating vitamin D. This creates the connection: Parathyroid Hormone regulates calcium metabolism. Its actions keep the bloodstream from dipping too low, especially when dietary calcium is insufficient.
Bone Health, the structural integrity and density of the skeletal system depends on a steady calcium supply. When calcium metabolism falters, bone density can fall, leading to osteoporosis. Osteoporosis represents the clinical outcome when the balance between bone formation and resorption is broken. Understanding this chain—calcium metabolism → bone health → osteoporosis—helps you spot early signs and act.
Understanding calcium metabolism gives you a clear picture of how vitamins, hormones, and bones interact to keep you strong. Below you’ll find articles that break down steroid effects, muscle relaxants, nutrition tips, and more—all tied back to the way your body handles calcium. Dive in to see practical advice, safety tips, and the latest research that can help you manage your health with confidence.
- October
17
2025 - 5
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism and GI Problems: What’s the Link?
Explore how secondary hyperparathyroidism triggers nausea, constipation, and other gut problems, and learn practical steps to manage both the hormonal disorder and digestive health.
Read More